Mars' Atmosphere Swells Dramatically Due to Solar Wind Variations
This remarkable occurrence was detected by NASA's MAVEN (Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution) orbiter, showcasing the intricate dynamics between the Martian atmosphere and the sun's behavior.
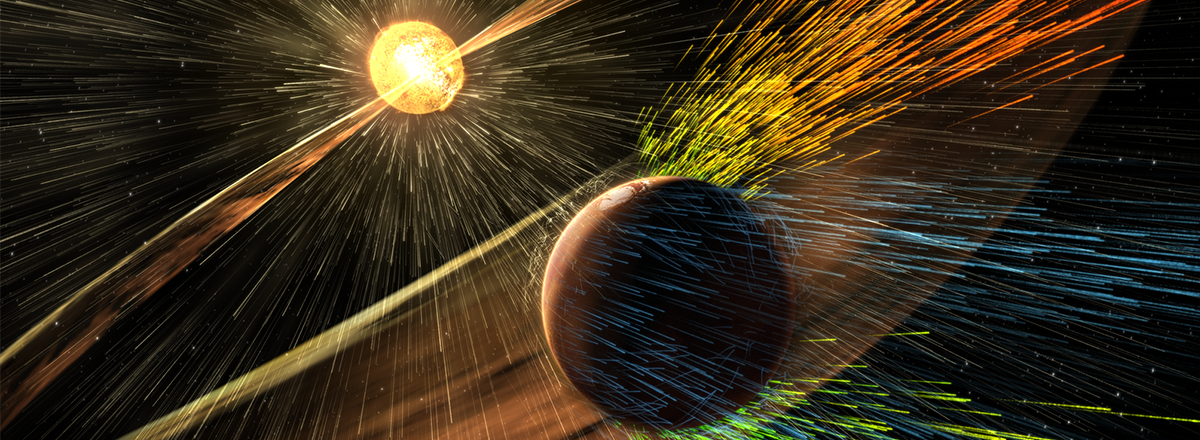
Mars' atmosphere experienced a significant expansion, resembling a balloon inflating, thanks to a temporary interruption in the solar wind. This remarkable occurrence was detected by NASA's MAVEN (Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution) orbiter, showcasing the intricate dynamics between the Martian atmosphere and the sun's behavior.
The typical scenario involves Mars losing about 0.25 lbs (0.11 kg) of its atmosphere every second due to the constant barrage of solar wind—a stream of charged particles originating from the sun. However, for a brief two-day period in December, the solar wind took an unusual hiatus. During this time, Mars' sunward side saw its atmosphere swell nearly fourfold, expanding from its usual 497 miles (800 km) to an astonishing 1,864 miles (3,000 km).
This unprecedented event was triggered when a fast-moving region of the solar wind overtook a slower counterpart, causing the latter to be swept away and creating an empty space. This rare occurrence reached Mars on December 25, 2022, offering scientists an extraordinary opportunity to witness the Martian atmosphere's dramatic expansion.
The insights gained from MAVEN's observations provide valuable data on how extreme solar events and their absence influence the Martian atmosphere, aiding in our understanding of its evolution.
Furthermore, these findings have implications for comprehending Earth-like planets beyond our solar system and how they interact with their host stars.

