A Massive Coronal Hole In the Sun's Surface Is Blasting Solar Wind Right at Earth
This phenomenon occurs as part of the Sun's natural activity cycle. While the Sun experiences periods of heightened solar activity, including sunspots or solar flares, it eventually reaches a peak known as solar maximum.
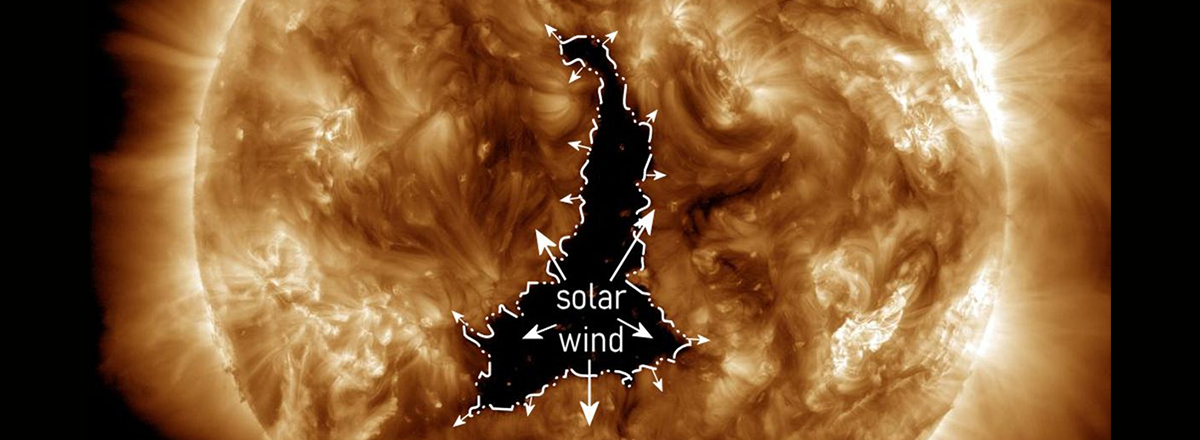
A colossal dark patch, known as a coronal hole, has emerged on the surface of the Sun, and its size is more than 60 times that of Earth. Positioned towards Earth, this coronal hole has the potential to influence our planet in various ways.
This enormous coronal hole on the Sun stretches approximately 800,000 kilometers in length, and astronomers are already detecting a stream of charged solar particles emanating from it, directed towards Earth. While this phenomenon might lead to disruptions in radio communication, especially at higher latitudes, it could also result in vibrant polar auroras, as reported by Space.com.
It's important to note that this massive dark patch isn't a literal "hole in the Sun." Astronomers refer to such areas as coronal holes, which are cooler regions in the Sun's outer atmosphere or corona. These areas have lower plasma temperatures compared to their surroundings, rendering them darker and observable primarily in ultraviolet and X-ray wavelengths.
Coronal holes have the potential to trigger powerful solar activities, such as solar winds. When these solar emissions interact with Earth's atmosphere, they can disturb atmospheric atoms and provoke polar auroras while interfering with radio communication due to their impact on Earth.
Astronomers predict that the current coronal hole's effects won't result in severe geomagnetic storms, and the impacts of solar activity are expected to be short-lived.
This phenomenon occurs as part of the Sun's natural activity cycle. While the Sun experiences periods of heightened solar activity, including sunspots, solar flares, and coronal mass ejections, it eventually reaches a peak known as solar maximum. We are currently approaching this peak in the Sun's approximately 11-year solar cycle, with solar maximum anticipated in early 2024.

