Scientists Confirmed the Composition of Mars's Core Using Seismic Waves
Scientists were able to confirm the composition of Mars's core using seismic waves that traveled through the Red Planet. It turned out that Mats has a liquid core made of iron alloy and high amounts of sulfur and oxygen.
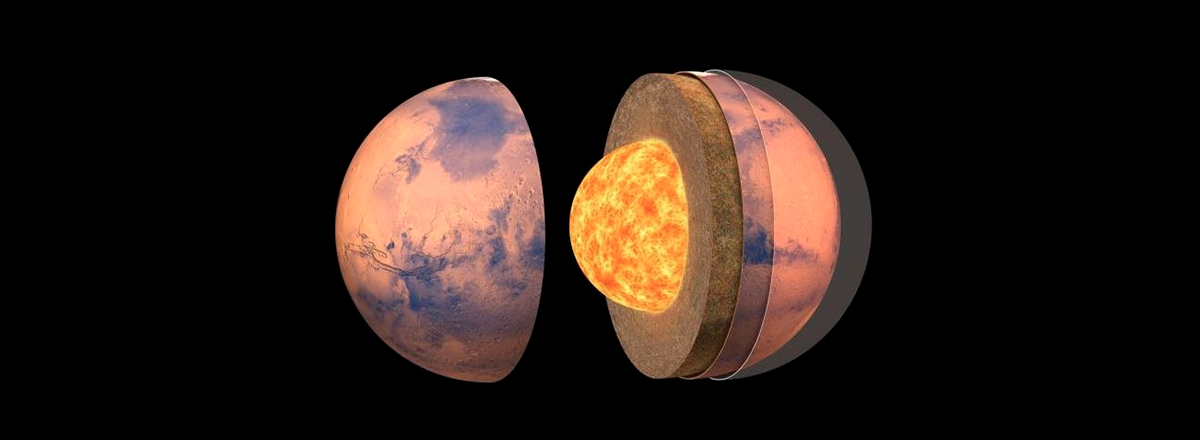
Using seismic data obtained by NASA's no longer operating InSight, scientists have been able to detect seismic waves traveling through the planet's core for the first time. It allowed them to understand and analyze the composition of Mars's core.
Scientists have discovered that the core of Mars is a liquid iron alloy — unlike the Earth's core, which consists of a liquid shell and a solid core. There are also surprisingly large amounts of sulfur and oxygen mixed in in the core of Mars. This means that the planet's core is less dense than Earth's, which could help scientists better understand the history of Mars and why it is so different from our Earth.
During its relatively short time monitoring the interior of Mars, InSight detected hundreds of marsquakes, giving scientists detailed information about the Martian interior. In 2021, InSight detected two tremendous events on Mars: a giant marsquake and a meteorite impact.
In 1906, scientists first discovered the Earth's core by observing how seismic waves from earthquakes were affected as they passed through it. More than a century later, the same knowledge was applied to Mars.

